The penis is the most delicate male organ. But men sometimes experience itching and painful genitalia.
Itching, discomfort, and burning in the penis can irritate and upset sufferers. There are times when a person’s foreskin is itchy, but no rash is present.
Why does my foreskin itch? Unfortunately, the answer to this question is often saught.
This sign is not always a sign of a severe health problem. However, anyone who experiences pain or discomfort around the foreskin should seek medical attention to avoid further harm.
Why Does My Foreskin Itch? Causes Of Itchy Foreskin
There are numerous causes of itchy, rash-free foreskin. Common causes include:
Balanitis
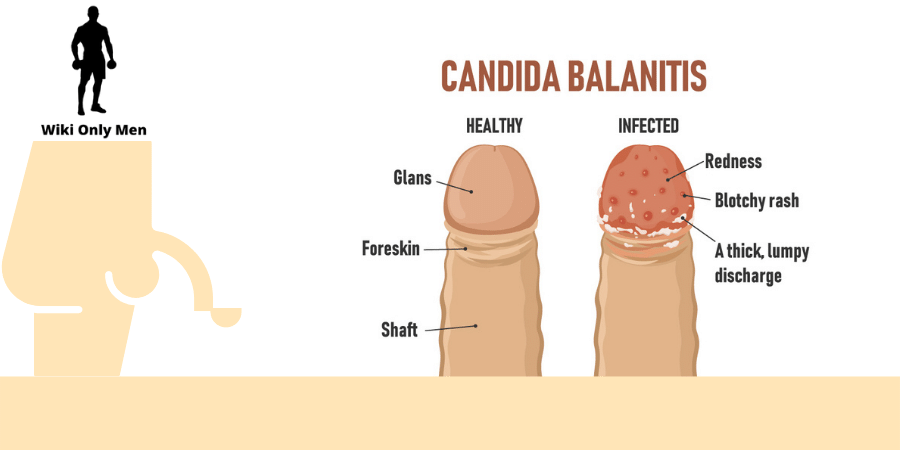
A yeast infection, medically known as candidiasis, can manifest in several body parts. For example, the yeast can grow under the foreskin because of the favorable environment.
Yeast infections can take many different forms. One type of yeast infection is balanitis, which causes itching on and around the penis. Jock itch is a superficial infection that causes itching in the groin area. However, it is generally accompanied by a rash.
Swelling or inflammation of the penis’s head is medically referred to as balanitis. While itchy foreskin without a rash can be caused by this disorder. However, rashes, discharge, uncomfortable urination, and difficulties sliding down the foreskin are all possible side effects.
You can have balanitis for many reasons, such as an allergic reaction or infection and improper cleanliness. Balanitis affects 11–13% of guys who are not circumcised. Regularly washing the penis, especially the inside of the foreskin, can help prevent irritation and infections.
However, even though balanitis is not considered a severe health issue, it dramatically raises the chance of developing penile cancer. Therefore, symptoms of balanitis should prompt anyone to seek medical attention.
Remedies
Your doctor will prescribe an antifungal cream like clotrimazole if a yeast infection is causing your balanitis. The cream must be applied to the glans and foreskin in the manner suggested.
The intensity of the inflammation, the underlying reason, and the patient’s age will all play a role in the therapy of balanitis. A variety of treatments are available for treatment, including:
- Use warm water and salt water to wash the penis.
- The use of hypoallergenic soaps in place of conventional soap.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs).
- A steroid and antifungal ointment.
- Antibiotics prescribed by your doctor may be necessary for more severe conditions.
- The frequency of diaper changes in newborns.
Latex Allergy

A latex allergy is an allergic reaction to natural rubber latex derived from the rubber tree sap (Hevea brasiliensis). Natural rubber latex is used in various items, including rubber exam gloves, balloons, and condoms.
Fewer than 1% of the general population in the United States suffer from latex allergy. But personnel in the medical field or occupations where latex is routinely encountered have a higher risk of developing latex allergies. Approximately 8% to 17% of those working in this sector are allergic to latex.
Individuals with latex allergies should avoid using any condoms that contain the substance.
Remedies
There is no specific therapy for latex allergies, but if you have them, you should avoid latex.
An allergist (a healthcare provider specializing in allergies) usually helps people with latex allergies. You can avoid an allergic reaction by changing your lifestyle and avoiding foods that may induce an allergic reaction.
Also, after using condoms, anyone who notices an itchy foreskin with no rash, itching, or swelling on their penis should switch to non-latex condoms.
Genital Herpes
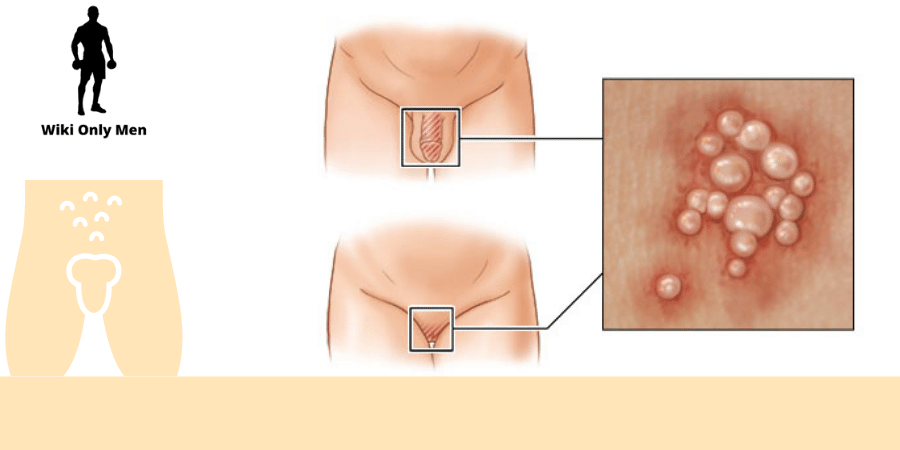
Herpes simplex virus-caused genital herpes affects more than 12 percent of people ages 14–49 in the United States.
Mild herpes symptoms frequently go unnoticed, although sores can form in the genital or oral regions where the virus was first encountered. And herpes is often misdiagnosed.
Genital herpes can also cause painful urination and itching around the genitals. Those experiencing these signs and symptoms should consult a doctor right away.
Remedies
Even though there is no cure for herpes at this time, antiviral medicines can help manage the symptoms. In fact, the CDC claims that these may even lessen the chances of it spreading from one person to another.
As with other STDs, the best way to prevent genital herpes is to avoid sexual contact. Sexual activity should be avoided or limited to only one individual who has not been infected.
- You and your partner should always use a condom during intercourse.
- Don’t have sex with someone who has herpes on the vaginal area or elsewhere.
Chlamydia
Chlamydia is caused by bacteria. Typically, the germs are transmitted by sexual contact or contact with infected genital secretions (semen or vaginal fluid). Unprotected sex (sex without using a condom) is the most common method of transmission, and sexually active teenagers and young adults are at the greatest risk.
STIs like chlamydia are a widespread cause of itchy foreskin. In the United States, the CDC estimates that 2.86 million people are infected with chlamydia each year, according to reliable sources.
Chlamydia can go undetected for a long period. However, it can induce an itchy foreskin without a rash in certain people. Pain when urinating and penile discharge are also possible symptoms. Testicles may become bloated and uncomfortable in some cases.
Remedies
Antibiotics are a successful treatment option. However, before engaging in sexual activity with another person, those with chlamydia should take the medication prescribed by their doctor.
If you are taking doxycycline, you should refrain from having intercourse (including oral sex) until you and your current sexual partner have completed your therapy.
If you’ve been given azithromycin, you should wait 7 days before having intercourse (including oral sex).
To help stop the spread of the infection, your present sexual partner and any other recent sexual partners should be tested and treated.
Three to six months after treatment, chlamydia patients under the age of 25 should be retested. This is because young adults who have chlamydia are more likely to catch it again.
Gonorrhea
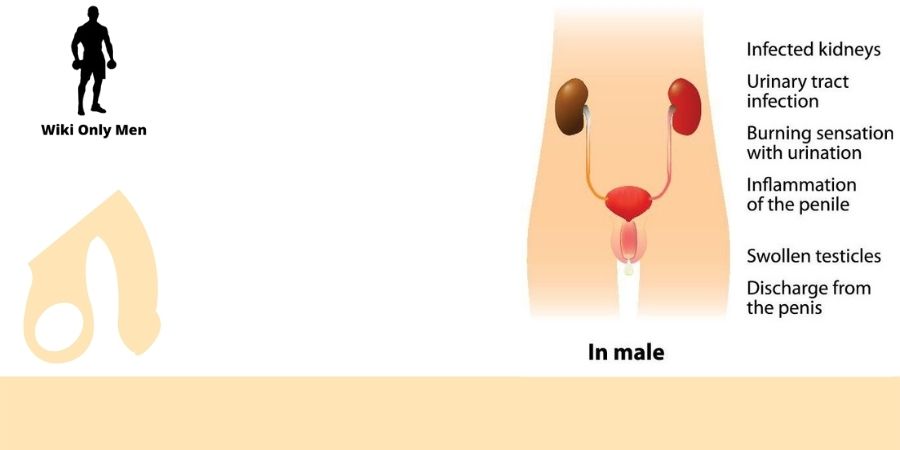
Sexual contact can spread gonorrhea, which is a bacterial STI. It is estimated by the CDC that 1.14 million new cases occur each year in the United States.
The majority of persons with gonorrhea don’t show any symptoms. However, pain or burning during urination and penile discharge from the penis are some signs when they do arise.
Remedies
Gonorrhea can be adequately treated with prescription medicine, but there is always a danger of reinfection.
Wrapping Up
Foreskin itching is a common symptom of various infections, including balanitis, yeast infections, and various sexually transmitted diseases (STIs). However, an itchy foreskin that isn’t accompanied by a rash can signify something more serious.
They usually react well to treatment but don’t usually improve on their own. Therefore, anyone experiencing severe, persistent, or alarming symptoms related to the penis should seek medical attention.

